Thanks for following SMS through another year of progress and transition as we push to commercialize products built on years of R&D. The biggest news from 2025 - we secured a strategic investment from Tokyo-based advanced materials leader Resonac! This investment, which came after more than three years of B2B co-development work, was a strong validation of our technology’s potential.
We also successfully completed two SBIRs focused on optical applications, including signature management for advanced stealth and high-efficiency solar panels for space systems. The development and commercialization work continues, but now we’re armed with advanced prototypes and product demos.
Last year also brought significant equipment upgrades, including customization of our roll-to-roll nanoimprint tool and ongoing improvements to our Nanocoining system.
The year ahead is shaping up to be exciting once again, as we accelerate commercialization, plan a move to larger lab space, and continue advanced R&D in defense and space.
Thanks again for the interest and support, and please drop a line with questions or updates for us!
Stephen
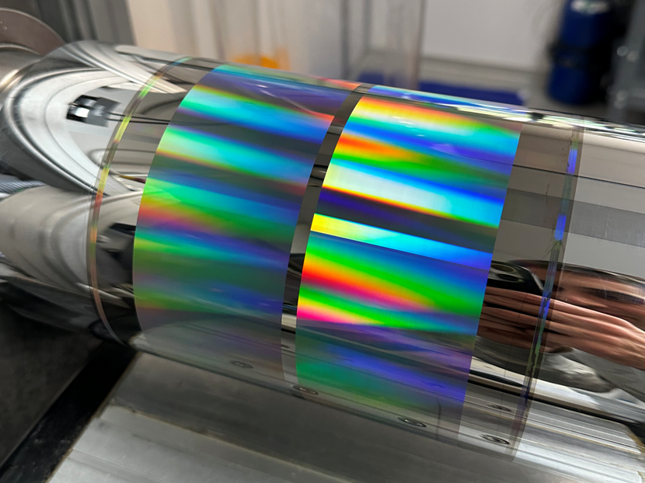
In-House Roll-to-Roll Nanoimprint Capability
This tool enables us to do pilot-scale (6” web) UV roll-to-roll nanoimprint lithography (R2R NIL) in the same room as our Nanocoining system for writing seamless molds.
Recent Projects - IR Camo
Our IR Camo Film is a highly scalable metasurface enabled by our abilities to create seamless drum molds and recent advances in image writing. The resulting material enables tunable variations in SWIR–LWIR emissivity, offering new pathways for thermal signature management.
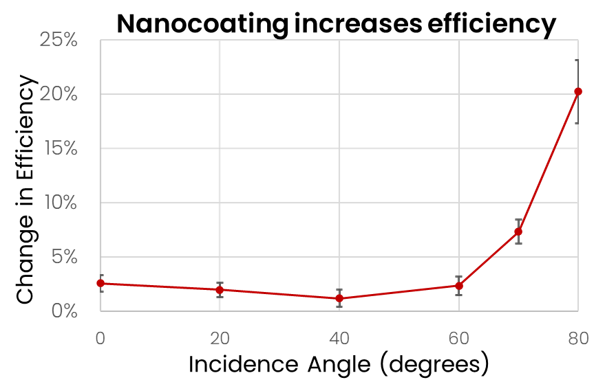
Recent Projects - Solar Enhancement
Building off our partnership with PowerFilm Solar to add encapsulation films to field-deployable solar panels, we joined forces with Microlink Devices to develop a light-trapping nanocoating for multijunction solar panels in low-Earth orbit. The coating outperforms state-of-the-art anti-reflective solar glass and lays the foundation for a domestic supplier of high-efficiency solar glass.
Recent Projects - Image Writing and Diffraction
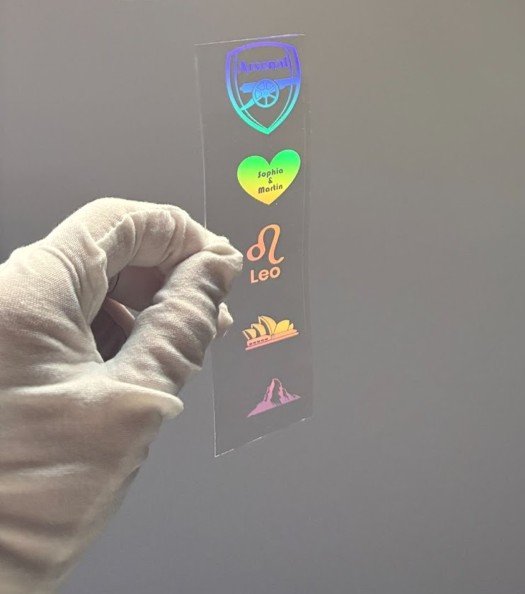
We continue to improve resolution and uniformity of diffractive color patterns based on sub-wavelength optics. These fuel applications in brand security, luxury goods marketing, and ink-free labeling.
Blogs from 2025
Upcoming Conferences
TechConnect World, Raleigh, NC. March 10-12, 2026.